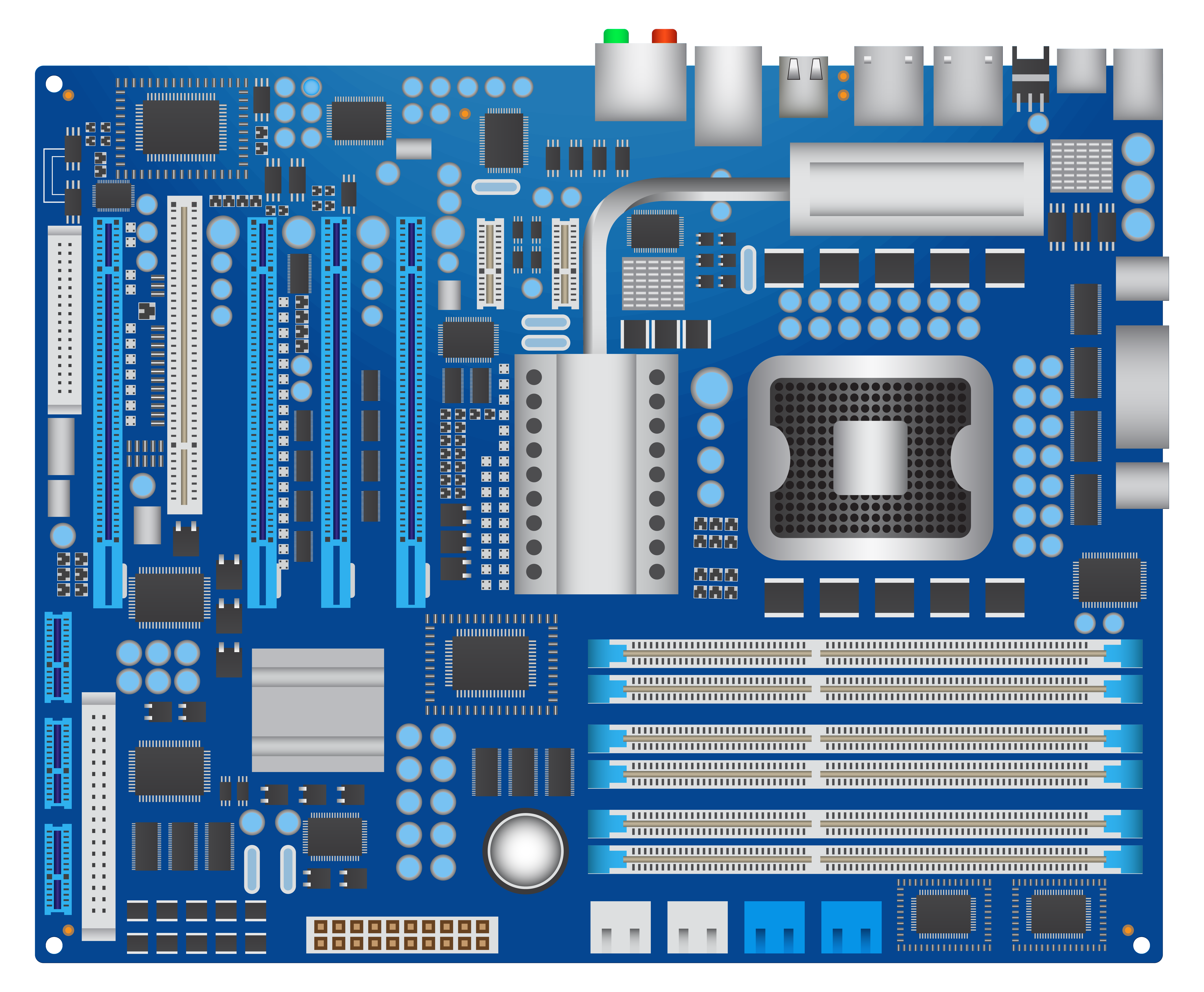
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer, connecting and enabling communication between the CPU, memory, storage, and other hardware components.
Specifications
Core Function
Acts as the main connection point for the CPU, memory, storage, and other peripherals.
Ensures seamless data transfer between components to enable smooth system operations.
Components and Connections
CPU Socket: Houses the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and determines compatibility with processors (e.g., Intel LGA, AMD AM4).
Memory Slots (RAM): Supports installation of RAM modules for temporary data storage.
Storage Interfaces:
SATA ports for Hard Drives (HDD) and Solid-State Drives (SSD).
NVMe/PCIe slots for high-speed M.2 SSDs.
Expansion Slots:
PCIe slots for graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
Power Connectors: Connects to the power supply unit (PSU) for system-wide power distribution.
Types of Motherboards
ATX: Standard-sized motherboard offering multiple expansion options.
Micro-ATX: Smaller, with fewer expansion slots, ideal for compact systems.
Mini-ITX: Compact and energy-efficient for small builds.
Connectivity Features
Input/Output (I/O) Ports: USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, and video outputs (HDMI, DisplayPort).
Onboard Networking: Integrated Ethernet or Wi-Fi modules for internet connectivity.
BIOS/UEFI Firmware: Provides low-level hardware control and system boot configuration.
Applications
Supports all components required for gaming, productivity, content creation, and server operations.
Enables future upgrades with expansion slots and ports.